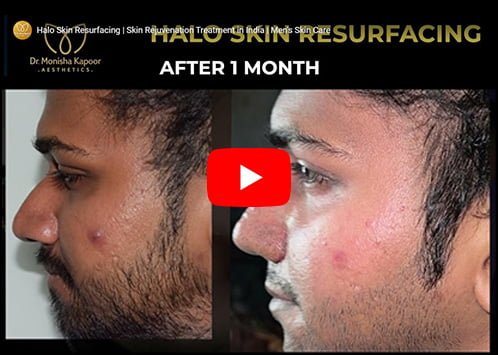
Rosacea
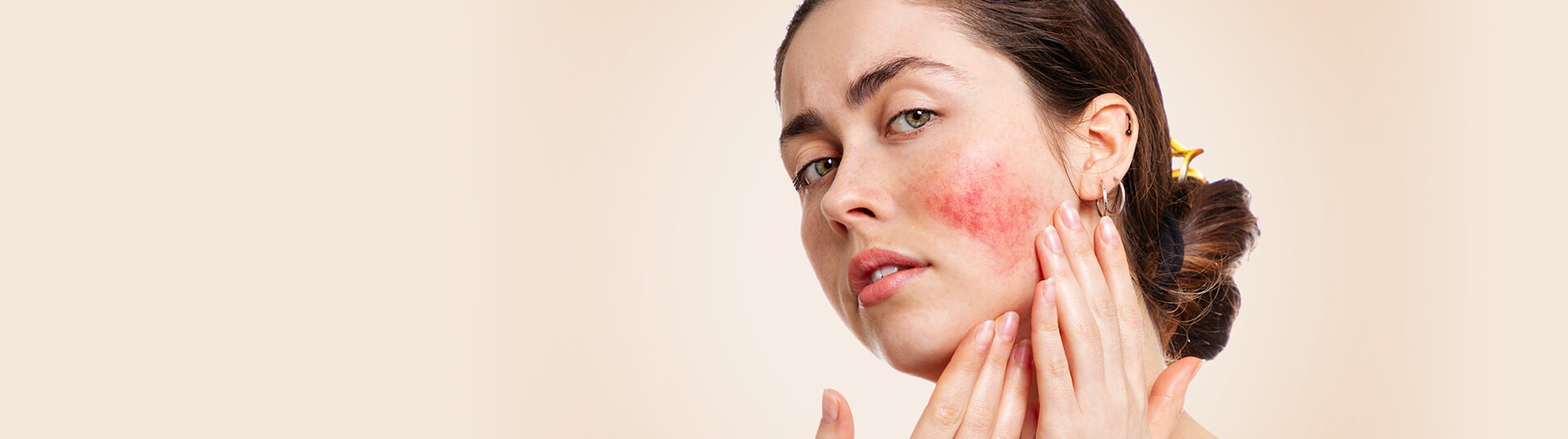
Rosacea is a common skin disease. It often begins with a tendency to blush or flush more easily than other people.
The redness can slowly spread beyond the nose and cheeks to the forehead and chin. Even the ears, chest, and back can be red all the time.
Rosacea can cause more than redness. There are so many signs and symptoms that rosacea has four subtypes.
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea- Redness, flushing, visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular rosacea- Redness, swelling, and acne-like breakouts.
- Phymatous rosacea- Skin thickens and has a bumpy texture.
- Ocular rosacea- Eyes red and irritated, eyelids can be swollen, and the person may have what looks like a sty.With time, people who have rosacea often see permanent redness in the center of their face.
if you have rosacea, laser or light therapy may be a part of your treatment plan. It’s unlikely to be your only treatment, though.

Different treatments for different signs of rosacea
When dermatologists create a treatment plan for rosacea, the plan often consists of medication, a rosacea friendly skin care plan, and tips to help you avoid flare-ups. Sometimes, a treatment plan also includes a procedure, such as laser therapy.
Your treatment plan is most likely to include a laser or light therapy if rosacea has caused:
- Visible blood vessels
- Thickening skin
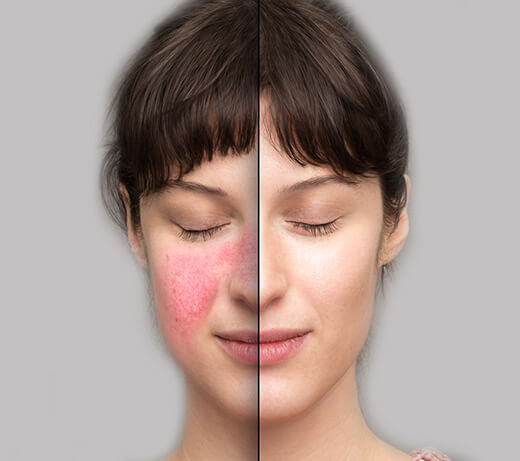
A laser or light treatment can reduce (or get rid of) the blood vessels. To remove thickening skin, dermatologists may use laser resurfacing.
Laser treatment can also reduce redness.
When used to treat visible blood vessels, most patients see a 50% to 75% reduction in visible blood vessels after 1 to 3 treatments. Some people see a 100% reduction.
Treatments are usually spaced 3 to 4 weeks apart.
If you have thickening skin, a skilled cosmetic dermatologist can give you very good results with in-office surgery and laser resurfacing. Patients who treat their thickening skin early tend to see the best results.
When used to treat blood vessels, the results tend to last 3 to 5 years. Treated blood vessels don’t reappear, but new ones can form.
Thickening skin tends to return after treatment. To prevent this and help you maintain results, your dermatologist can prescribe medication. You may also need follow-up laser therapy in the future.